从需求去理解 Linux dbus与基于dbus协议的无agent软件管理
2021/9/13 7:05:07
本文主要是介绍从需求去理解 Linux dbus与基于dbus协议的无agent软件管理,对大家解决编程问题具有一定的参考价值,需要的程序猿们随着小编来一起学习吧!
What is IPC
IPC [Inter-Process Communication] 进程间通信,指至少两个进程或线程间传送数据或信号的一些技术或方法。在Linux/Unix中,提供了许多IPC。Unix七大IPC:
- Pipe:无名管道,最基本的IPC,单向通信,仅在父/子进程之间,也就是将一个程序的输出直接交给另一个程序的输入。常见使用为
ps -ef|grep xxx - FIFO [
(First in, First out)] 或 有名管道(named pipe):与Pipe不同,FIFO可以让两个不相关的进程可以使用FIFO。单向。 - Socket 和 Unix Domain Socket:socket和Unix套接字,双向。适用于网络通信,但也可以在本地使用。适用于不同的协议。
- 消息队列
Message Queue: SysV 消息队列、POSIX 消息队列。 - Signal: 信号,是发送到正在运行的进程通知以触发其事件的特定行为,是IPC的一种有限形式。
- Semaphore:信号量,通常用于IPC或同一进程内的线程间通信。他们之间使用队列进行消息传递、控制或内容的传递。(常见SysV 信号量、POSIX 信号量)
- Shared memory:(常见SysV 共享内存、POSIX 共享内存)。共享内存,是在进程(程序)之间传递数据的有效方式,目的是在其之间提供通信。
每种IPC都有不通的特点,每种方式对资源的使用及性能都是不通的
- 管道 I/O是最快的,但为单向通信,需要工作在 父/子 进程关系之间。
- UNIX 套接字可以在本地连接不同的进程,并且具有更高的带宽,并且没有固有的消息边界。
- TCP/IP套接字可以连接任何进程。并且可以通过网络连接,但是对资源会有更多的开销,同样的没有固定的消息边界。
Reference
comparsion Unix/Linux IPC
What is D-Bus
提到,D-Bus就不能不提一下freedesktop,而 D-Bus 仅仅作为freedesktop.org的一部分。
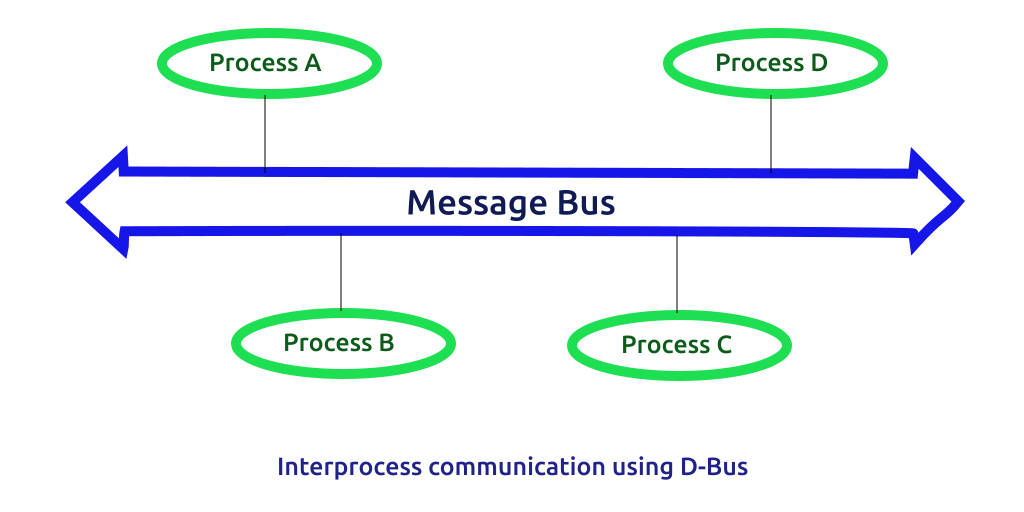
D-Bus 桌面总线 (Desktop Bus),的简写,也是Linux- IPC机制,不同于Unix 7大基础IPC的是,D-Bus是在这些IPC类型之上实现的中间件IPC,D-Bus使用了基础IPC中一种过多种,其设计的目的是在Linux桌面环境,提供服务的标准化。但目前并没有合入主线内核中。
作为中间件IPC,D-Bus的性能较低与其他IPC模式,因为在通信过程中会进行很多上下文切换,如果通过Dbus来发送消息,会先将其发送到内核,然后将其送回D-Bus。AF_BUS 补丁是新的套接字类型,用来减少D-Bus上下文的切换。
更多可参考:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D-Bus
D-Bus组成
D-Bus是 一个IPC的实现方式,在架构上分位三层。
- Layer 1 libdbus:freedesktop机构提供的一个免费开源的一个由C语言编写的
low-level API。是提供dbus功能的库。是高级API绑定的低级API。 - Layer 2 dbus daemon:dbus实现的IPC守护进行,随Linux启动,通过不通进程对其的连接,实现了多进程间消息的路由(包含内核、网络、桌面等)
- Layer 3 Wapper libraries (high-level API): 对
low-level APIlibdbus的封装 ,例如libdbus-qtlibdbus-pythongithub.com/godbus/dbus,这些不同编程语言实现的Wapper是不同开发者应该使用的lib,其简化了D-Bus的开发难度。
Reference
dbus-tutorial
dbus 基本概念
总线
在 D-Bus 中,bus是一个核心概念。它是应用程序可以进行方法调用、发送信号和侦听信号的通道。有两种预定义的bus:会话总线和系统总线。
-
会话总线(Session Bus):普通进程创建,可同时存在多条。会话总线属于某个进程私有,它用于进程间传递消息。
-
系统总线(System Bus):在引导时就会启动,它由操作系统和后台进程使用,安全性非常好,以使得任意的应用程序不能欺骗系统事件。当然,如果一个应用程序需要接受来自系统总线的消息,他也可以直接连接到系统总线中,但是他能发送的消息是受限的。系统总线最常见的用途是在系统范围事件发生时发送系统范围的通知。添加新的存储设备、网络连接更改事件和关闭相关事件都是系统总线何时更适合通信总线的示例。
通常情况下只存在一个System Bus,但可以存在多个Session Bus(每个桌面会话一个)。
总线以dbus-daemon的形式存在与系统中,该进程专门将消息从一个进程传递到另一个进程。该守护进程还将向总线上的所有应用程序转发通知。
bus name
总线名称 Bus Name,不能单单以字面意思 总线名称 来理解,官方对其解释为:Connections have one or more bus names associated with them. A connection has exactly one bus name that is a unique connection name.,可以出bus name其实是用来连接名称。主要是用来标识一个应用和消息总线的连接。总线名称主要分为两类:唯一名称与公共名称。
- 唯一连接名称
unique connection names:以冒号(':')字符开头的 bus name是唯一的连接名称。例如:1.0。每个连接都有一个唯一名。在一个 消息总线的生命期内,不会有两个连接有相同的唯一名。 - 公共连接名称
well-known bus names:公共名称是以反向DNS域名(小写)例如:org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1。- 如果DNS 域名包含连字符/减号,则应将其替换为下划线,如果包含数字,则应通过添加下划线进行转义。例如: 7-zip.org的bus name应该定义为
org._7_zip.Archiver。
- 如果DNS 域名包含连字符/减号,则应将其替换为下划线,如果包含数字,则应通过添加下划线进行转义。例如: 7-zip.org的bus name应该定义为
Reference
bus name
对象路径
对象路径(Object Paths) 是用于引用对象实例的名称(类似于 C++ 或 Java 对象)。从概念上来说,D-Bus在消息交换中每个参与者都有任意个对象实例,如文件系统一样,Dbus中的参与者中的对象实例也会形成一个层次树。如,在CentOS7中 firewalld开发的D-Bus API 使用了/org/fedoraproject/FirewallD1的层次结构。
在定义一个对象路径时,需要注意以下:
- 路径可以是任意长度
- 路径必须以 ASCII '/'(整数 47)字符开头,并且必须由以斜杠字符分隔的元素组成。
- 每个元素只能包含 ASCII 字符
[AZ][az][0-9]_ - 不允许出现 空字符串
- 多个
/字符不能依次出现。 除非路径是根路径(单个/字符),否则不允许尾随/字符。
接口名称
interface,在每个 Object Path都包含多个接口,一般情况下接口名称应以反向 DNS 域名开头(小写),(同 Java 中的接口名称)。在命名规则上,与bus name相同。
例如:CentOS7中 firewalld开发的D-Bus API 定义的管理zone的接口 org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.config.zone。如果DNS名称中包含-,则应将其替换为下划线 _。如果DNS 域名包含紧跟在 . 之后的数字,则接口名称应在数字之前添加一个下划线。例如,如果 7-zip.org 插件定义了一个接口,应该被命名为org._7_zip.Plugin.
成员方法名称
成员方法名称,Member names ,对于定义了接口后,需要实现其接口的放法,如需要获得firewalld的zone时,就可以调用 org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.getDefaultZone 。在D-Bus中Member names通常由“驼峰式”(camel-case)命名 。
dbus
在Linux中,如CentOS dbus包括 dbus daemon及一些cli commad。这些包
dbuslib
D-Bus的消息
最基本的D-Bus协议是一对一的通信协议。与直接使用socket不同,D-Bus是面向消息的协议。 D-Bus的所有功能都是通过在连接上流动的消息完成的。
而在D-Bus中有四种类型的消息
- METHOD_CALL 方法调用
- METHOD_RETURN 方法返回
- ERROR 错误
- SIGNAL 信号:与方法调用不同,信号发射没有响应。信号发射只是一个类型为
SIGNAL的消息。它必须具有三个标头字段:PATH给出发出信号的对象,加上INTERFACE并MEMBER给出信号的完全限定名称。
消息返回的类型
| Conventional name | 十进制值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
INVALID |
0 | 这是个无效类型 |
METHOD_CALL |
1 | 方法调用,该方法会有提示 |
METHOD_RETURN |
2 | 方法返回的数据 |
ERROR |
3 | 错误返回,第一个是其错误的信息 |
SIGNAL |
4 | 信号的发射 |
CentOS的dbus服务管理
在CentOS7中,作为systemd的一部分D-BUS会从Systemd获取套接字文件描述符,并使用D-Bus交换当前进程生成的socket信息。而PID 1 不使用 PolicyKit 来控制对特权操作的访问,而是完全依赖于 low-level API D-Bus 。(这样做是为了避免 PolicyKit 和 systemd/PID 1 之间的循环依赖。)而有些特权进程(例如关机/重启/挂起/登陆)可以通过logind进行管理的。
由此,可以知道在CentOS中,dbus相关的服务大概有 dbus,与 logind。
dbus包含:
-
dbus-daemon:dbus架构中 layer 2的 dbus-damon
-
dbus-send: dbus提供的命令行工具,可以用dbus-send来发送消息。
-
dbus-monitor: dbus提供的命令行工具,用于监视总线上流动的消息。
-
dbus-launch: shell脚本启动消息总线的命令行工具
dbus配置文件说明
dbus-daemon守护进程,有两个配置文件,一个为 session bus,另外一个为 system bus。
标准的system bus文件 /usr/local/share/dbus-1/system.conf session bus配置 /usr/local/share/dbus-1/session.conf中配置。在一般情况下,不会操作这两个文件,因其会引入 /etc/dbus-1 中的system.conf 或 session.conf。
配置文件包含的标签:
更多的注释可以参考:dbus-daemon
# 根元素
<busconfig>
<!-- 根据指定的 -system或 -session 来选择的配置文件 -->
<type>system</type>
<!-- dbus-daemon运行的用户 -->
<user>dbus</user>
<!-- Fork into daemon mode -->
<fork/>
<!-- We use system service launching using a helper -->
<standard_system_servicedirs/>
<!-- This is a setuid helper that is used to launch system services -->
<servicehelper>//usr/libexec/dbus-1/dbus-daemon-launch-helper</servicehelper>
<!-- Write a pid file -->
<pidfile>/run/dbus/messagebus.pid</pidfile>
<!-- Enable logging to syslog -->
<syslog/>
<!-- 指定授权机制。如果不存在,所有的机制都被允许。 -->
<auth>EXTERNAL</auth>
<!-- 总线监听的地址,支持unix socket,tcp,system等
-->
<listen>unix:path=/run/dbus/system_bus_socket</listen>
<listen>unix:path=/tmp/foo</listen>
<listen>tcp:host=localhost,port=1234</listen>
<policy context="default">
<!-- All users can connect to system bus -->
<allow user="*"/>
<!-- Holes must be punched in service configuration files for
name ownership and sending method calls -->
<deny own="*"/>
<deny send_type="method_call"/>
<!-- Signals and reply messages (method returns, errors) are allowed
by efault -->
<allow send_type="signal"/>
<allow send_requested_reply="true" send_type="method_return"/>
<allow send_requested_reply="true" send_type="error"/>
<!-- All messages may be received by default -->
<allow receive_type="method_call"/>
<allow receive_type="method_return"/>
<allow receive_type="error"/>
<allow receive_type="signal"/>
<!-- Allow anyone to talk to the message bus -->
<allow send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.DBus" />
<allow send_destination="org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1"
send_interface="org.fedorapproject.FirewallD1" />
<allow send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable"/>
<!-- But disallow some specific bus services -->
<deny send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_member="UpdateActivationEnvironment"/>
<deny send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.DBus.Debug.Stats"/>
<deny send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.systemd1.Activator"/>
</policy>
<!-- Only systemd, which runs as root, may report activation failures. -->
<policy user="root">
<allow send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.systemd1.Activator"/>
</policy>
<!-- root may monitor the system bus. -->
<policy user="root">
<allow send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.DBus.Monitoring"/>
</policy>
<!-- If the Stats interface was enabled at compile-time, root may use it.
Copy this into system.local.conf or system.d/*.conf if you want to
enable other privileged users to view statistics and debug info -->
<policy user="root">
<allow send_destination="org.freedesktop.DBus"
send_interface="org.freedesktop.DBus.Debug.Stats"/>
</policy>
<!-- Include legacy configuration location -->
<include ignore_missing="yes">/etc/dbus-1/system.conf</include>
<!-- 包含的子配置文件. -->
<includedir>system.d</includedir>
<includedir>/etc/dbus-1/system.d</includedir>
<!-- This is included last so local configuration can override what's
in this standard file -->
<include ignore_missing="yes">/etc/dbus-1/system-local.conf</include>
<include if_selinux_enabled="yes" selinux_root_relative="yes">contexts/dbus_contexts</include>
</busconfig>
通过命令行发送dbus消息
dbus支持通过命令发送一个dbus消息,如获取可用的dbus 服务。
dbus-send --session \
--dest=org.freedesktop.DBus \
--type=method_call \
--print-reply \
/org/freedesktop/DBus \
org.freedesktop.DBus.ListNames
method return time=1631452206.288425 sender=org.freedesktop.DBus -> destination=:1.29 serial=3 reply_serial=2
array [
string "org.freedesktop.DBus"
string "org.freedesktop.login1"
string "org.freedesktop.systemd1"
string "org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1"
string "org.freedesktop.PolicyKit1"
string ":1.17"
string ":1.0"
string ":1.29"
string ":1.18"
string ":1.1"
]
返回org.freedesktop.DBus service
dbus-send --session \ --dest=org.freedesktop.DBus \ --type=method_call \ --print-reply \ /org/freedesktop/DBus \ org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable.Introspect
使用dbus api操作linux防火墙
Firewalld是一个基于动态区域的防火墙守护进程,自 2009 年左右开始开发,目前为Fedora 18 以及随后的 RHEL7 和 CentOS 7 中的默认防火墙机制。
Firewalld被配置为systemd D-Bus 服务。请注意下面的“Type=dbus”指令。
# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service [Unit] Description=firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Before=network.target Before=libvirtd.service Before=NetworkManager.service Conflicts=iptables.service ip6tables.service ebtables.service [Service] EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/firewalld ExecStart=/usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid $FIREWALLD_ARGS ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID # supress to log debug and error output also to /var/log/messages StandardOutput=null StandardError=null Type=dbus BusName=org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1 [Install] WantedBy=basic.target Alias=dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service
知道了firewalld服务是基于D-Bus的,就可以通过D-Bus来操作防火墙。
查看dbus注册的服务是否包含firewalld,这里需要注意的是,firewalld依赖dbus服务,每次启动firewalld时注册到dbus总线内。所以需要先启动dbus-daemon与 firewalld 服务。
dbus-send --system --dest=org.freedesktop.DBus --type=method_call --print-reply \ /org/freedesktop/DBus org.freedesktop.DBus.ListNames | grep FirewallD
查看得知 org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1 为firewalld接口
查看接口所拥有的方法、属性、信号等信息
dbus-send --system --dest=org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1 --print-reply \ /org/fedoraproject/FirewallD1 org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable.Introspect
获得zone
firewall-cmd --get-zones dbus-send --system \ --dest=org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1 \ --print-reply \ --type=method_call /org/fedoraproject/FirewallD1 \ org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.zone.getZones
查看zone内的条目信息
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-all dbus-send --system --dest=org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1 --print-reply --type=method_call \ /org/fedoraproject/FirewallD1 org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.getZoneSettings string:"public"
这篇关于从需求去理解 Linux dbus与基于dbus协议的无agent软件管理的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对大家有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持为之网!
- 2024-12-18git仓库有更新,jenkins 自动触发拉代码怎么配置的?-icode9专业技术文章分享
- 2024-12-18Jenkins webhook 方式怎么配置指定的分支?-icode9专业技术文章分享
- 2024-12-13Linux C++项目实战入门教程
- 2024-12-13Linux C++编程项目实战入门教程
- 2024-12-11Linux部署Scrapy教程:新手入门指南
- 2024-12-11怎么将在本地创建的 Maven 仓库迁移到 Linux 服务器上?-icode9专业技术文章分享
- 2024-12-10Linux常用命令
- 2024-12-06谁看谁服! Linux 创始人对于进程和线程的理解是…
- 2024-12-04操作系统教程:新手入门及初级技巧详解
- 2024-12-04操作系统入门:新手必学指南





