使用Kubernetes简化分布式Spring Boot应用中的定时任务管理
2024/11/15 2:03:03
本文主要是介绍使用Kubernetes简化分布式Spring Boot应用中的定时任务管理,对大家解决编程问题具有一定的参考价值,需要的程序猿们随着小编来一起学习吧!
这个标题遵循了通俗易懂和符合中文口语表达习惯的要求,同时准确地反映了文章的核心内容。
定时任务非常常见,我们经常会遇到它们来完成不同的任务。
在Spring Boot应用中,传统上大家经常会用到@Scheduled。采用这种做法时,Spring将负责定时任务的调度及执行。这种简单的方法当只有一个应用实例运行时效果非常好。
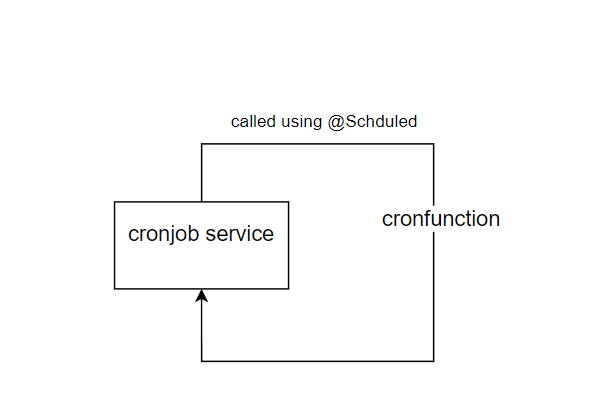
使用 @Schedule 的单个 Cronjob 服务
我们来看一个简单的例子:
包 com.blogs.services;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ExampleService {
@Scheduled(cron = "* * * * * *")
public void cronfunction() {
System.out.println("执行cron任务");
}
}
我们的 cronfunction() 每隔一分钟通过 Spring 的 @Scheduled 注解被自动调用。
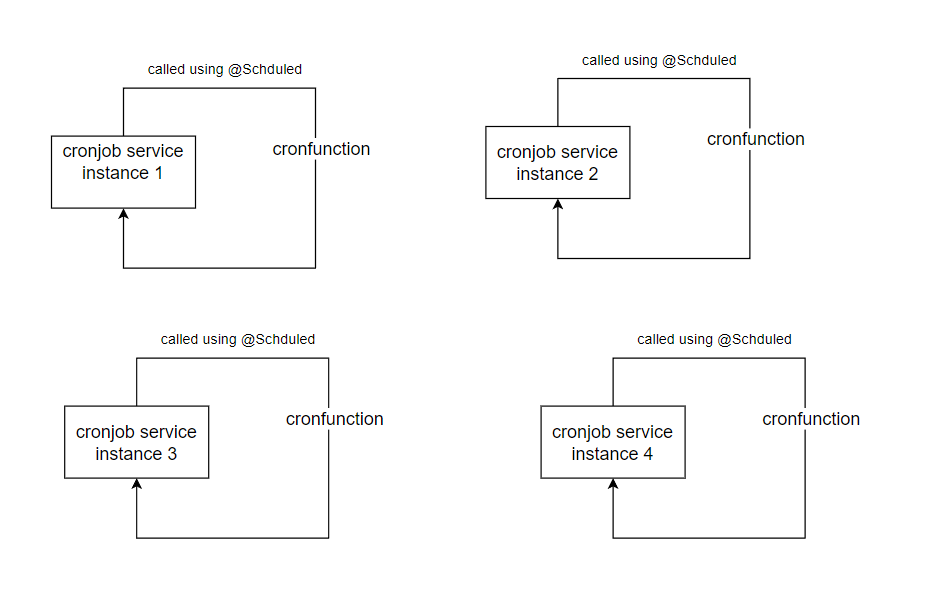
一个运行着4个实例的cronjob定时任务服务
如上图所示,您将在4个实例上运行相同的定时任务,这可能会导致竞态条件、重复操作以及增加资源使用量。
如果此定时任务执行的是清理数据库记录这样的操作,将引发异常,因为四个应用将尝试访问相同的数据库记录,假设所有4个实例执行的操作相同。这也会导致数据库不一致。
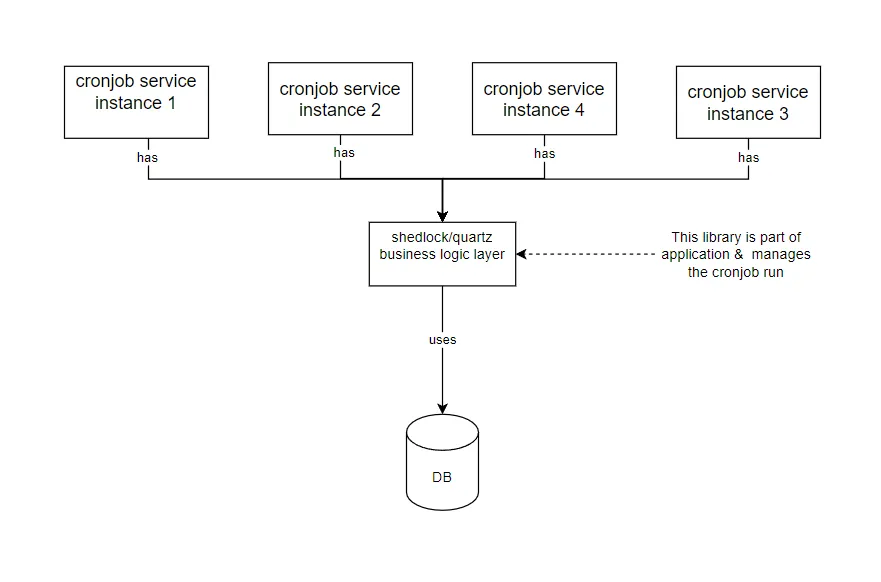
这些问题可以通过诸如 Shedlocks 和 Quartz-scheduler 这样的工具来解决。它们使用外部数据库来管理计划作业,以确保只有一个应用实例运行定时任务。
用Quartz或Shedlock简单理解定时作业
这种方法的缺点在于需要额外的资源投入来在平台上同步定时任务的运行,还需要一个数据库表来记录定时任务的运行情况。
使用 Kubernetes 的 CronJob,我们可以在不使用明确指定的数据库的情况下处理这个问题。
使用 API 端点暴露(方法一)
这种方法既简单又容易理解和实现。我们在SpringBoot应用程序中通过一个API接口公开CronJob函数。然后利用Kubernetes CronJob来调用这个API接口。当系统采用水平扩展时,负载均衡器通常会自动平衡传入的CronJob API请求。
Kubernetes CronJob 的 API 终点
第一步是?暴露一个API端点来在Spring应用中执行定时任务。
package com.blogs.controllers;
import com.blogs.services.ExampleService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController
public class ExampleController { @Autowired
ExampleService exampleService; @PostMapping(path = "/cronjob")
public void runCronJob(){
// 运行定时任务
exampleService.cronfunction();
}
}
然后我们创建一个 Kubernetes CronJob, 来使用 curl 调用这个端点。
apiVersion: batch/v1 # API 版本
kind: CronJob # 定时任务
metadata:
name: cronjob-test # 任务名称
spec:
schedule: "* * * * *" # 定时任务的调度时间
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: hello # 容器名称
image: busybox:1.28 # 使用的镜像
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent # 镜像拉取策略
command:
- /bin/sh # 使用 shell
- -c # shell 参数
- curl -X POST http://example.com/cronjob # 发送 POST 请求到指定 URL
restartPolicy: OnFailure # 失败时重启
# "OnFailure" 表示任务失败时将会重启
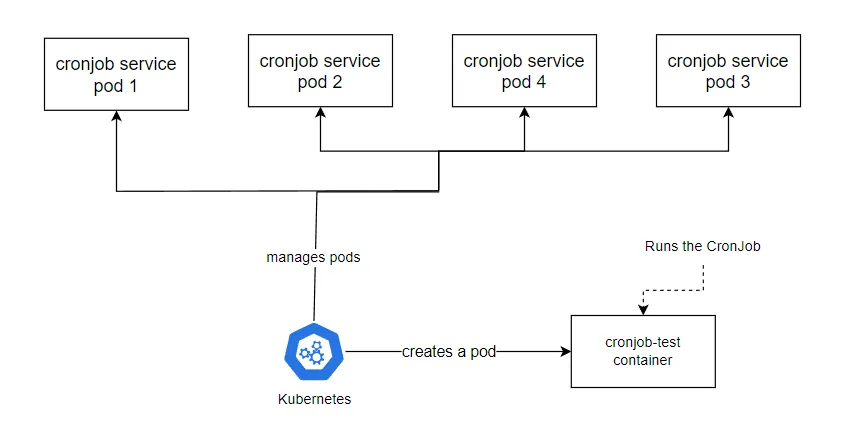
Kubernetes 根据 JobTemplate 创建新的 Pod,其中运行的是 CronJob。如果安全是必要的,可以使用 gRPC 或 Thrift 的 RPC 调用来实现。否则,可以创建一个 Docker 镜像来运行 bash 脚本,以执行身份验证并调用端点。
每次 CronJob 需要运行时,都会创建一个新的应用 Pod。目的是为 Spring Boot 应用提供一个备用执行点来运行 CronJob,并通过设置环境变量来控制其执行。
Kubernetes CronJob 任务使用备选入口点
我们对SpringBoot应用的主函数进行了如下修改。首先,使用应用的ApplicationContext来运行CronJob,然后在任务执行完毕后通过System.exit(0);退出容器。使用退出码0变得相当必要,否则应用将以错误退出,否则Kubernetes将不会认为应用运行成功。
包 com.blogs;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import com.blogs.services.ExampleService;
import java.util.Optional;
@SpringBootApplication
public class CronjobApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(CronjobApplication.class, args);
Optional.ofNullable(System.getenv("runcronjob")).ifPresent(arg -> {
System.out.println("存在的话");
if(arg.equals("true")){
System.out.println("如果是true");
try(applicationContext){
System.out.println("尝试运行cronjob任务");
ExampleService exampleService = applicationContext.getBean(ExampleService.class);
exampleService.cronfunction();
System.out.println("cronjob执行完毕");
} catch (BeansException e){
System.out.println("获取bean时出错");
}
System.out.println("退出容器环境");
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
Kubernetes CronJob yaml 使用应用程序的 Docker 镜像以及环境变量 runcronjob 来管理 CronJob 任务的执行。基本模板如下:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: cronjob
spec:
schedule: "* * * * *"
concurrencyPolicy: Forbid
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: cronjob
image: blogs/cronjob:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: runcronjob
value: "true"
restartPolicy: Never
我们也可以为 CronJob 类创建独立的配置,因为这类配置专门用于执行定时任务。
如果应用程序很大,并且包含数据库连接池、缓存连接池、消息队列连接等配置,应用程序启动时将消耗大量资源。因此,如果一个CronJob在启动时不需要应用程序启动时那么多的资源,那么创建API端点会更有意义。
尽管 Kubernetes CronJob 提供了简单性和灵活性,但在选择上述方法时,还是要考虑具体的应用场景。这些方法也适用于大多数 Java 框架,如 Micronaut、Dropwizard 等。
可以在这里查看 SpringBoot 应用代码 here ,以及在这里查看 Helm Chart 仓库 here。
- https://github.com/quartz-scheduler/quartz 一个开源的Quartz调度器项目
- https://github.com/lukas-krecan/ShedLock
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/cron-jobs/ Kubernetes 定时任务工作负载概念
- https://thenewstack.io/rethinking-java-scheduled-tasks-in-kubernetes/ 重新思考 Kubernetes 中的 Java 定时任务
- https://github.com/jad837/cronjob 一个用于管理定时任务的GitHub项目
- https://github.com/jad837/cronjob-helm 一个用于 Helm 安装定时任务的 GitHub 项目
这篇关于使用Kubernetes简化分布式Spring Boot应用中的定时任务管理的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对大家有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持为之网!
- 2024-12-21Kubernetes生产环境问题排查指南:实战教程
- 2024-12-20使用Encore.ts构建和部署TypeScript微服务到Kubernetes集群
- 2024-12-20Kubernetes:从理念到1.0的历程
- 2024-12-18第28天:Kubernetes中的蓝绿部署讲解
- 2024-12-15从零到Kubernetes安全大师:简化集群安全防护
- 2024-12-15掌握Kubernetes节点调度:污点、容忍、节点选择器和节点亲和性
- 2024-12-14第五天:与容器互动
- 2024-12-11CKA(Kubernetes管理员认证)速查表
- 2024-12-08.NET Aspire应用部署到Azure和Kubernetes实战指南
- 2024-12-07云原生周报:K8s未来三大发展方向不容错过