如何利用Shell脚本进行Linux服务器之CentOS7系统初始化及其安全加固(适用于等保2.0)
2022/4/13 3:12:36
本文主要是介绍如何利用Shell脚本进行Linux服务器之CentOS7系统初始化及其安全加固(适用于等保2.0),对大家解决编程问题具有一定的参考价值,需要的程序猿们随着小编来一起学习吧!
CentOS7 系统初始化安全加固
描述: 适用于企业内部 CentOS7 系列服务器操作系统初始化、系统安全加固脚本,内容包含了,网络初始化设置,软件更新源替换以及内核版本升级 ,时间时区初始化设置 系统安全加固(符合等保三级主机测评项) 安全运维设置 、系统内核参数优化、 常用软件安装等 一系列的操作直接开箱即用, 将跑过该脚本的机器可以克隆成为作为线上生产环境的基线模板。
原文链接: 完整的Windows与Linux服务器系统安全加固实践和基线检测脚本(等保2.0)
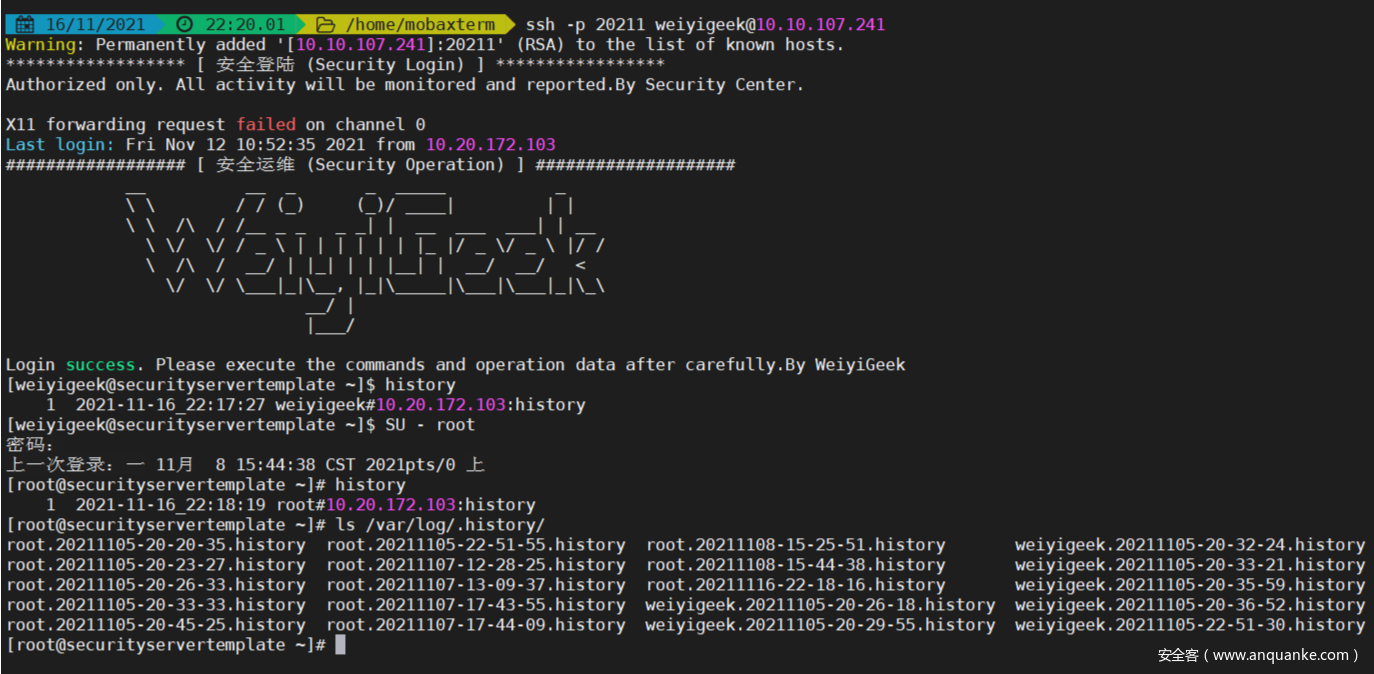
CentOS7 安全加固效果
项目地址: https://github.com/WeiyiGeek/SecOpsDev/tree/master/OS-操作系统/Linux/CentOS
【欢迎大家 Star 与 Fork 】
CentOS7 TLS Security Initiate
Link: https://github.com/WeiyiGeek/SecOpsDev/blob/master/OS-操作系统/Linux/CentOS/7/CentOS7-InitializeSecurity.sh
温馨提示: 使用脚本时请按照你的需求调用相应函数即可。
#!/bin/bash
# @Author: WeiyiGeek
# @Description: CentOS7 TLS Security Initiate
# @Create Time: 2019年5月6日 11:04:42
# @Last Modified time: 2021-11-15 11:06:31
# @E-mail: master@weiyigeek.top
# @Blog: https://www.weiyigeek.top
# @wechat: WeiyiGeeker
# @Github: https://github.com/WeiyiGeek/SecOpsDev/tree/master/OS-操作系统/Linux/
# @Version: 3.3
## ----------------------------------------- ##
# 脚本主要功能说明:
# (1) CentOS7系统初始化操作包括IP地址设置、基础软件包更新以及安装加固。
# (2) CentOS7系统容器以及JDK相关环境安装。
# (3) CentOS7系统中异常错误日志解决。
# (4) CentOS7系统中常规服务安装配置,加入数据备份目录。
# (4) CentOS7脚本错误解决和优化
## ----------------------------------------- ##
## 系统全局变量定义
# [系统配置]
HOSTNAME=CentOS-Security-Template
EXECTIME=$(date +%Y%m%d-%m%S)
# [网络配置]
IPADDR=192.168.1.2
NETMASK=225.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.1.1
DNSIP=("223.5.5.5" "223.6.6.6")
SSHPORT=20211
# [用户设置]
DefaultUser="WeiyiGeek" # 系统创建的用户名称非root用户
ROOTPASS=WeiyiGeek # 密码建议12位以上且包含数字、大小写字母以及特殊字符。
APPPASS=WeiyiGeek
# [SNMP配置]
SNMP_user=WeiyiGeek
SNMP_group=testgroup
SNMP_view=testview
SNMP_password=dont_use_public
SNMP_ip=127.0.0.1
# [配置备份目录]
BACKUPDIR=/var/log/.backups
if [ ! -d ${BACKUPDIR} ];then mkdir -vp ${BACKUPDIR}; fi
# [配置记录目录]
HISDIR=/var/log/.history
if [ ! -d ${HISDIR} ];then mkdir -vp ${HISDIR}; fi
## 名称: err 、info 、warning
## 用途:全局Log信息打印函数
## 参数: $@
log::err() {
printf "[$(date +'%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S')]: \033[31mERROR: $@ \033[0m\n"
}
log::info() {
printf "[$(date +'%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S')]: \033[32mINFO: $@ \033[0m\n"
}
log::warning() {
printf "[$(date +'%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S')]: \033[33mWARNING: $@ \033[0m\n"
}
## 名称: os::Network
## 用途: 操作系统网络配置相关脚本包括(IP地址修改)
## 参数: 无
os::Network(){
log::info "[-] 操作系统网络配置相关脚本,开始执行....."
# (1) 静态网络IP地址设置
tee /opt/network.sh <<'EOF'
#!/bin/bash
IPADDR="${1}"
NETMASK="${2}"
GATEWAY="${3}"
DEVNAME="ifcfg-ens192"
if [ "${4}" != "" ];then
DEVNAME="ifcfg-${4}"
fi
if [[ $# -lt 3 ]];then
echo -e "\e[32m[*] Usage: $0 IP-Address MASK Gateway \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[32m[*] Usage: $0 192.168.1.99 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 \e[0m"
exit 1
fi
NET_FILE="/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/${DEVNAME}"
if [[ ! -f ${NET_FILE} ]];then
log::err "[*] Not Found ${NET_FILE} File"
exit 2
fi
cp ${NET_FILE}{,.bak}
sed -i -e 's/^ONBOOT=.*$/ONBOOT="yes"/' -e 's/^BOOTPROTO=.*$/BOOTPROTO="static"/' ${NET_FILE}
grep -q "^IPADDR=.*$" ${NET_FILE} && sed -i "s/^IPADDR=.*$/IPADDR=\"${IPADDR}\"/" ${NET_FILE} || echo "IPADDR=\"${IPADDR}\"" >> ${NET_FILE}
grep -q "^NETMASK=.*$" ${NET_FILE} && sed -i "s/^NETMASK=.*$/NETMASK=\"${NETMASK}\"/" ${NET_FILE} || echo "NETMASK=\"${NETMASK}\"" >> ${NET_FILE}
grep -q "^GATEWAY=.*$" ${NET_FILE} && sed -i "s/^GATEWAY=.*$/IPADDR=\"${GATEWAY}\"/" ${NET_FILE} || echo "GATEWAY=\"${GATEWAY}\"" >> ${NET_FILE}
EOF
chmod +x /opt/network.sh
/opt/network.sh ${IPADDR} ${NETMASK} ${GATEWAY}
# (2) 系统主机名与本地解析设置
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname ${HOSTNAME}
# sed -i "s/127.0.1.1\s.\w.*$/127.0.1.1 ${NAME}/g" /etc/hosts
cp -a /etc/hosts ${BACKUPDIR}/hosts.bak
grep -q "^\$(hostname -I)\s.\w.*$" /etc/hosts && sed -i "s/\$(hostname -I)\s.\w.*$/${IPADDR} ${HOSTNAME}" /etc/hosts || echo "${IPADDR} ${HOSTNAME}" >> /etc/hosts
# (3) 系统DNS域名解析服务设置
cp -a /etc/resolv.conf ${BACKUPDIR}/resolv.conf.bak
for dns in ${DNSIP[@]};do echo "nameserver ${dns}" >> /etc/resolv.conf;done
log::info "[*] network configure modifiy successful! restarting Network........."
service network restart && ip addr
}
## 名称: os::Software
## 用途: 操作系统软件包管理及更新源配置相关脚本
## 参数: 无
os::Software () {
log::info "[-] 操作系统软件包管理及更新源配置相关脚本,开始执行....."
cp -a /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo ${BACKUPDIR}/CentOS-Base.repo
# (1) CentOS 软件仓库镜像源配置&&初始化更新
log::info "[*] CentOS 软件仓库镜像源配置&&初始化更新 "
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
sed -i "s#mirrors.cloud.aliyuncs.com#mirrors.aliyun.com#g" /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
rpm --import http://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
yum clean all && yum makecache
yum --exclude=kernel* update -y && yum upgrade -y && yum -y install epel*
# (2) CentOS 操作系统内核升级(可选)
cp -a /etc/grub2.cfg ${BACKUPDIR}/grub2.cfg.kernelupdate.bak
log::info "[*] CentOS 操作系统内核升级(可选) "
rpm --import https://www.elrepo.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-elrepo.org
yum -y install https://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm
yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel repolist
yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel list kernel*
# 内核安装,服务器里我们选择长期lt版本,安全稳定是我们最大的需求,除非有特殊的需求内核版本需求;
yum update -y --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel
# 内核版本介绍, lt:longterm 的缩写长期维护版, ml:mainline 的缩写最新主线版本;
yum install -y --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel --skip-broken kernel-lt kernel-lt-devel kernel-lt-tools
# yum -y --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel --skip-broken install kernel-ml.x86_64 kernel-ml-devel.x86_64 kernel-ml-tools.x86_64
log::warning "[*] 当前 CentOS 操作系统可切换的内核内核版本"
awk -F \' '$1=="menuentry " {print i++ " : " $2}' /etc/grub2.cfg
sudo grub2-set-default 0
#传统引导
# grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
# grubby --default-kernel
reboot
# (3) 安装常用的运维软件
# 编译软件
yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ g++ make jq libpam-cracklib openssl-devel bzip2-devel
# 常规软件
yum install -y nano vim git unzip wget ntpdate dos2unix net-tools
yum install -y tree htop ncdu nload sysstat psmisc bash-completion fail2ban nfs-utils chrony
# 清空缓存和已下载安装的软件包
yum clean all
log::info "[*] Software configure modifiy successful!Please Happy use........."
}
## 名称: os::TimedataZone
## 用途: 操作系统系统时间时区配置相关脚本
## 参数: 无
os::TimedataZone() {
log::info "[*] 操作系统系统时间时区配置相关脚本,开始执行....."
# (1) 时区设置东8区
log::info "[*] 时区设置前的时间: $(date -R) "
timedatectl
cp -a /etc/localtime ${BACKUPDIR}/localtime.bak
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
# (2) 时间同步软件安装
grep -q "192.168.12.254" /etc/chrony.conf || sudo tee -a /etc/chrony.conf <<'EOF'
pool 192.168.12.254 iburst maxsources 1
pool 192.168.10.254 iburst maxsources 1
pool 192.168.4.254 iburst maxsources 1
pool ntp.aliyun.com iburst maxsources 4
keyfile /etc/chrony.keys
driftfile /var/lib/chrony/chrony.drift
logdir /var/log/chrony
maxupdateskew 100.0
rtcsync
makestep 1.0 3
#stratumweight 0.05
#noclientlog
#logchange 0.5
EOF
systemctl enable chronyd && systemctl restart chronyd && systemctl status chronyd -l
# 将当前的 UTC 时间写入硬件时钟 (硬件时间默认为UTC)
sudo timedatectl set-local-rtc 0
# 启用NTP时间同步:
timedatectl set-ntp yes
# 时间服务器连接查看
chronyc tracking
# 手动校准-强制更新时间
# chronyc -a makestep
# 硬件时钟(系统时钟同步硬件时钟 )
hwclock --systohc
# 备用方案: 采用 ntpdate 进行时间同步 ntpdate 192.168.10.254
# (3) 重启依赖于系统时间的服务
sudo systemctl restart rsyslog.service crond.service
log::info "[*] Tie confmigure modifiy successful! restarting chronyd rsyslog.service crond.service........."
timedatectl
}
## 名称: os::Security
## 用途: 操作系统安全加固配置脚本(符合等保要求-三级要求)
## 参数: 无
os::Security () {
log::info "[-] 操作系统安全加固配置(符合等保要求-三级要求)"
# (0) 系统用户及其终端核查配置
log::info "[-] 锁定或者删除多余的系统账户以及创建低权限用户"
# cat /etc/passwd | cut -d ":" -f 1 | tr '\n' ' '
defaultuser=(root bin daemon adm lp sync shutdown halt mail operator games ftp nobody systemd-network dbus polkitd sshd postfix chrony ntp rpc rpcuser nfsnobody)
for i in $(cat /etc/passwd | cut -d ":" -f 1,7);do
flag=0; name=${i%%:*}; terminal=${i##*:}
if [[ "${terminal}" == "/bin/bash" || "${terminal}" == "/bin/sh" ]];then
log::warning "${i} 用户,shell终端为 /bin/bash 或者 /bin/sh"
fi
for j in ${defaultuser[@]};do
if [[ "${name}" == "${j}" ]];then
flag=1
break;
fi
done
if [[ $flag -eq 0 ]];then
log::warning "${i} 非默认用户"
fi
done
cp -a /etc/shadow ${BACKUPDIR}/shadow-${EXECTIME}.bak
passwd -l adm&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l daemon&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l bin&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l sys&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l lp&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l uucp&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l nuucp&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l smmsplp&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l mail&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l operator&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l games&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l gopher&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l ftp&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l nobody&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l nobody4&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l noaccess&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l listen&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l webservd&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l rpm&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l dbus&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l avahi&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l mailnull&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l nscd&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l vcsa&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l rpc&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l rpcuser&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l nfs&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l sshd&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l pcap&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l ntp&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l haldaemon&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l distcache&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l webalizer&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l squid&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l xfs&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l gdm&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l sabayon&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null; passwd -l named&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null
# (2) 用户密码设置和口令策略设置
log::info "[-] 配置满足策略的root管理员密码 "
echo "root:${ROOTPASS}" | chpasswd
log::info "[-] 配置满足策略的app普通用户密码(根据需求配置)"
groupadd application
useradd -m -s /bin/bash -c "application primary user" -g application app
echo "root:${APPPASS}" | chpasswd
log::info "[-] 强制用户在下次登录时更改密码 "
chage -d 0 -m 0 -M 90 -W 15 root && passwd --expire root
chage -d 0 -m 0 -M 90 -W 15 app && passwd --expire app
chage -d 0 -m 0 -M 90 -W 15 ${DefaultUser} && passwd --expire ${DefaultUser}
log::info "[-] 用户口令复杂性策略设置 (密码过期周期0~90、到期前15天提示、密码长度至少15、复杂度设置至少有一个大小写、数字、特殊字符、密码三次不能一样、尝试次数为三次)"
# 相关修改文件备份
cp /etc/login.defs ${BACKUPDIR}/login.defs.bak;
cp /etc/pam.d/password-auth ${BACKUPDIR}/password-auth.bak
cp /etc/pam.d/system-auth ${BACKUPDIR}/system-auth.bak
egrep -q "^\s*PASS_MIN_DAYS\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$" /etc/login.defs && sed -ri "s/^(\s*)PASS_MIN_DAYS\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$/\PASS_MIN_DAYS 0/" /etc/login.defs || echo "PASS_MIN_DAYS 0" >> /etc/login.defs
egrep -q "^\s*PASS_MAX_DAYS\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$" /etc/login.defs && sed -ri "s/^(\s*)PASS_MAX_DAYS\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$/\PASS_MAX_DAYS 90/" /etc/login.defs || echo "PASS_MAX_DAYS 90" >> /etc/login.defs
egrep -q "^\s*PASS_WARN_AGE\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$" /etc/login.defs && sed -ri "s/^(\s*)PASS_WARN_AGE\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$/\PASS_WARN_AGE 15/" /etc/login.defs || echo "PASS_WARN_AGE 15" >> /etc/login.defs
egrep -q "^\s*PASS_MIN_LEN\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$" /etc/login.defs && sed -ri "s/^(\s*)PASS_MIN_LEN\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$/\PASS_MIN_LEN 15/" /etc/login.defs || echo "PASS_MIN_LEN 15" >> /etc/login.defs
egrep -q "^password\s.+pam_pwquality.so\s+\w+.*$" /etc/pam.d/password-auth && sed -ri '/^password\s.+pam_pwquality.so/{s/pam_pwquality.so\s+\w+.*$/pam_pwquality.so try_first_pass local_users_only retry=3 authtok_type= minlen=15 ucredit=-1 lcredit=-1 dcredit=-1 ocredit=-1 difok=1 enforce_for_root/g;}' /etc/pam.d/password-auth
egrep -q "^password\s.+pam_unix.so\s+\w+.*$" /etc/pam.d/password-auth && sed -ri '/^password\s.+pam_unix.so/{s/pam_unix.so\s+\w+.*$/pam_unix.so sha512 shadow nullok try_first_pass use_authtok remember=3/g;}' /etc/pam.d/password-auth
egrep -q "^password\s.+pam_pwquality.so\s+\w+.*$" /etc/pam.d/system-auth && sed -ri '/^password\s.+pam_pwquality.so/{s/pam_pwquality.so\s+\w+.*$/pam_pwquality.so try_first_pass local_users_only retry=3 authtok_type= minlen=15 ucredit=-1 lcredit=-1 dcredit=-1 ocredit=-1 difok=1 enforce_for_root/g;}' /etc/pam.d/system-auth
egrep -q "^password\s.+pam_unix.so\s+\w+.*$" /etc/pam.d/system-auth && sed -ri '/^password\s.+pam_unix.so/{s/pam_unix.so\s+\w+.*$/pam_unix.so sha512 shadow nullok try_first_pass use_authtok remember=3/g;}' /etc/pam.d/system-auth
log::info "[-] 存储用户密码的文件,其内容经过sha512加密,所以非常注意其权限"
# 解决首次登录配置密码时提示"passwd: Authentication token manipulation error"
touch /etc/security/opasswd && chown root:root /etc/security/opasswd && chmod 600 /etc/security/opasswd
# (3) 设置用户sudo权限以及重要目录和文件的新建默认权限
log::info "[-] 用户sudo权限以及重要目录和文件的新建默认权限设置"
cp /etc/sudoers ${BACKUPDIR}/sudoers.bak
# 如CentOS安装时您创建的用户 WeiyiGeek 防止直接通过 sudo passwd 修改root密码(此时必须要求输入WeiyiGeek密码后才可修改root密码)
# Tips: Sudo允许授权用户权限以另一个用户(通常是root用户)的身份运行程序,
# DefaultUser="weiyigeek"
sed -i "/# Allows members of the/i ${DefaultUser} ALL=(ALL) PASSWD:ALL" /etc/sudoers
# 此参数需要根据业务来定,否则在使用时候会出现某些权限不足导致程序安装报错
log::info "[-] 配置用户 umask 为022 "
cp -a /etc/profile ${BACKUPDIR}/profile
egrep -q "^\s*umask\s+\w+.*$" /etc/profile && sed -ri "s/^\s*umask\s+\w+.*$/umask 022/" /etc/profile || echo "umask 022" >> /etc/profile
# log::info "[-] 设置用户目录创建默认权限, (初始为077比较严格)在未设置umask为027则默认为077"
# egrep -q "^\s*umask\s+\w+.*$" /etc/csh.login && sed -ri "s/^\s*umask\s+\w+.*$/umask 022/" /etc/csh.login || echo "umask 022" >> /etc/csh.login
# egrep -q "^\s*umask\s+\w+.*$" /etc/csh.cshrc && sed -ri "s/^\s*umask\s+\w+.*$/umask 022/" /etc/csh.cshrc || echo "umask 022" >> /etc/csh.cshrc
# egrep -q "^\s*(umask|UMASK)\s+\w+.*$" /etc/login.defs && sed -ri "s/^\s*(umask|UMASK)\s+\w+.*$/UMASK 027/" /etc/login.defs || echo "UMASK 027" >> /etc/login.defs
log::info "[-] 设置或恢复重要目录和文件的权限(设置日志文件非全局可写)"
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys;
chmod 755 /etc;
chmod 755 /etc/passwd;
chmod 755 /etc/shadow;
chmod 755 /etc/security;
chmod 644 /etc/group;
chmod 644 /etc/services;
chmod 750 /etc/rc*.d;
chmod 755 /var/log/messages;
chmod 775 /var/log/spooler;
chmod 775 /var/log/cron;
chmod 775 /var/log/secure;
chmod 775 /var/log/maillog;
chmod 775 /var/log/mail&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null;
chmod 775 /var/log/localmessages&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null
log::info "[-] 删除潜在威胁文件 "
find / -maxdepth 3 -name hosts.equiv | xargs rm -rf
find / -maxdepth 3 -name .netrc | xargs rm -rf
find / -maxdepth 3 -name .rhosts | xargs rm -rf
# (4) SSHD 服务安全加固设置以及网络登陆Banner设置
log::info "[-] sshd 服务安全加固设置"
cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config ${BACKUPDIR}/sshd_config.bak
# 严格模式
sudo egrep -q "^\s*StrictModes\s+.+$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && sed -ri "s/^(#)?\s*StrictModes\s+.+$/StrictModes yes/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config || echo "StrictModes yes" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# 默认的监听端口更改
if [ -e ${SSHPORT} ];then export SSHPORT=20211;fi
sudo egrep -q "^\s*Port\s+.+$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && sed -ri "s/^(#)?\s*Port\s+.+$/Port ${SSHPORT}/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config || echo "Port ${SSHPORT}" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# 禁用X11转发以及端口转发
sudo egrep -q "^\s*X11Forwarding\s+.+$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && sed -ri "s/^(#)?\s*X11Forwarding\s+.+$/X11Forwarding no/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config || echo "X11Forwarding no" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
sudo egrep -q "^\s*X11UseLocalhost\s+.+$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && sed -ri "s/^(#)?\s*X11UseLocalhost\s+.+$/X11UseLocalhost yes/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config || echo "X11UseLocalhost yes" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
sudo egrep -q "^\s*AllowTcpForwarding\s+.+$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && sed -ri "s/^(#)?\s*AllowTcpForwarding\s+.+$/AllowTcpForwarding no/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config || echo "AllowTcpForwarding no" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
sudo egrep -q "^\s*AllowAgentForwarding\s+.+$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && sed -ri "s/^(#)?\s*AllowAgentForwarding\s+.+$/AllowAgentForwarding no/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config || echo "AllowAgentForwarding no" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# 关闭禁用用户的 .rhosts 文件 ~/.ssh/.rhosts 来做为认证: 缺省IgnoreRhosts yes
egrep -q "^(#)?\s*IgnoreRhosts\s+.+$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && sed -ri "s/^(#)?\s*IgnoreRhosts\s+.+$/IgnoreRhosts yes/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config || echo "IgnoreRhosts yes" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# 禁止root远程登录(推荐配置-根据需求配置)
egrep -q "^\s*PermitRootLogin\s+.+$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && sed -ri "s/^\s*PermitRootLogin\s+.+$/PermitRootLogin no/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config || echo "PermitRootLogin no" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# 登陆前后欢迎提示设置
egrep -q "^\s*(banner|Banner)\s+\W+.*$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && sed -ri "s/^\s*(banner|Banner)\s+\W+.*$/Banner \/etc\/issue/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config || \
echo "Banner /etc/issue" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
log::info "[-] 远程SSH登录前后提示警告Banner设置"
# SSH登录前后提示警告Banner设置
sudo tee /etc/issue <<'EOF'
****************** [ 安全登陆 (Security Login) ] *****************
Authorized only. All activity will be monitored and reported.By Security Center.
EOF
# SSH登录后提示Banner
# 艺术字B格: http://www.network-science.de/ascii/
sudo tee /etc/motd <<'EOF'
################## [ 安全运维 (Security Operation) ] ####################
__ __ _ _ _____ _
\ \ / / (_) (_)/ ____| | |
\ \ /\ / /__ _ _ _ _| | __ ___ ___| | __
\ \/ \/ / _ \ | | | | | | |_ |/ _ \/ _ \ |/ /
\ /\ / __/ | |_| | | |__| | __/ __/ <
\/ \/ \___|_|\__, |_|\_____|\___|\___|_|\_\
__/ |
|___/
Login success. Please execute the commands and operation data after carefully.By WeiyiGeek
EOF
# (5) 用户远程登录失败次数与终端超时设置
log::info "[-] 用户远程连续登录失败10次锁定帐号5分钟包括root账号"
cp /etc/pam.d/sshd ${BACKUPDIR}/sshd.bak
cp /etc/pam.d/login ${BACKUPDIR}/login.bak
# 远程登陆
sed -ri "/^\s*auth\s+required\s+pam_tally2.so\s+.+(\s*#.*)?\s*$/d" /etc/pam.d/sshd
sed -ri '2a auth required pam_tally2.so deny=10 unlock_time=300 even_deny_root root_unlock_time=300' /etc/pam.d/sshd
# 宿主机控制台登陆(可选)
# sed -ri "/^\s*auth\s+required\s+pam_tally2.so\s+.+(\s*#.*)?\s*$/d" /etc/pam.d/login
# sed -ri '2a auth required pam_tally2.so deny=10 unlock_time=300 even_deny_root root_unlock_time=300' /etc/pam.d/login
log::info "[-] 设置登录超时时间为10分钟 "
egrep -q "^\s*(export|)\s*TMOUT\S\w+.*$" /etc/profile && sed -ri "s/^\s*(export|)\s*TMOUT.\S\w+.*$/export TMOUT=600\nreadonly TMOUT/" /etc/profile || echo -e "export TMOUT=600\nreadonly TMOUT" >> /etc/profile
egrep -q "^\s*.*ClientAliveInterval\s\w+.*$" /etc/ssh/sshd_config && sed -ri "s/^\s*.*ClientAliveInterval\s\w+.*$/ClientAliveInterval 600/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config || echo "ClientAliveInterval 600" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# (6) 切换用户日志记录和切换命令更改名称为SU
log::info "[-] 切换用户日志记录和切换命令更改名称为SU "
cp -a /etc/rsyslog.conf ${BACKUPDIR}/rsyslog.conf-${EXECTIME}.bak
egrep -q "^\s*authpriv\.\*\s+.+$" /etc/rsyslog.conf && sed -ri "s/^\s*authpriv\.\*\s+.+$/authpriv.* \/var\/log\/secure/" /etc/rsyslog.conf || echo "authpriv.* /var/log/secure" >> /etc/rsyslog.conf
egrep -q "^(\s*)SULOG_FILE\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$" /etc/login.defs && sed -ri "s/^(\s*)SULOG_FILE\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$/\SULOG_FILE \/var\/log\/.history\/sulog/" /etc/login.defs || echo "SULOG_FILE /var/log/.history/sulog" >> /etc/login.defs
egrep -q "^\s*SU_NAME\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$" /etc/login.defs && sed -ri "s/^(\s*)SU_NAME\s+\S*(\s*#.*)?\s*$/\SU_NAME SU/" /etc/login.defs || echo "SU_NAME SU" >> /etc/login.defs
mkdir -vp /usr/local/bin
cp /usr/bin/su ${BACKUPDIR}/su.bak
mv /usr/bin/su /usr/bin/SU
chmod 777 /var/log/.history
chattr -R +a /var/log/.history
chattr +a /var/log/.backups
# (7) 用户终端执行的历史命令记录
log::info "[-] 用户终端执行的历史命令记录 "
egrep -q "^HISTSIZE\W\w+.*$" /etc/profile && sed -ri "s/^HISTSIZE\W\w+.*$/HISTSIZE=101/" /etc/profile || echo "HISTSIZE=101" >> /etc/profile
sudo tee /etc/profile.d/history-record.sh <<'EOF'
# 历史命令执行记录文件路径
LOGTIME=$(date +%Y%m%d-%H-%M-%S)
export HISTFILE="/var/log/.history/${USER}.${LOGTIME}.history"
if [ ! -f ${HISTFILE} ];then
touch ${HISTFILE}
fi
chmod 600 /var/log/.history/${USER}.${LOGTIME}.history
# 历史命令执行文件大小记录设置
HISTFILESIZE=128
HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F_%T $(whoami)#$(who -u am i 2>/dev/null| awk '{print $NF}'|sed -e 's/[()]//g'):"
EOF
# (8) GRUB 安全设置
log::info "[-] 系统 GRUB 安全设置(防止物理接触从grub菜单中修改密码) "
# Grub 关键文件备份
cp -a /etc/grub.d/00_header ${BACKUPDIR}/'00_header'${EXECTIME}.bak
cp -a /etc/grub.d/10_linux ${BACKUPDIR}/'10_linux'${EXECTIME}.bak
# 设置Grub菜单界面显示时间
sed -i -e 's|set timeout_style=${style}|#set timeout_style=${style}|g' -e 's|set timeout=${timeout}|set timeout=3|g' /etc/grub.d/00_header
# sed -i -e 's|GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE=hidden|#GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE=hidden|g' -e 's|GRUB_TIMEOUT=0|GRUB_TIMEOUT=3|g' /etc/default/grub
# grub 用户认证密码创建
sudo grub2-mkpasswd-pbkdf2
# 输入口令:
# Reeter password:n
PBKDF2 hash of your password is grub.pbkdf2.sha512.10000.A4A6B06EFAB660C11DD8EBC3BE73C5AB5D763ED937060477DB533B3E7D60F1DE66C3AC12DA795B46762AB8C4A1911B69B94FFCD88FB4499938150405DCB116F8.35D290F5B8D2677AEE5E8BAB4DB133206D417F99A26B14EAB8D0A5379DCD3632F40037388C9D2CA3001E0D6A8B74837549970EEEAEC3420CE38E2236DE1A8565
# 设置认证用户以及上面生成的password_pbkdf2认证密钥
tee -a /etc/grub.d/00_header <<'END'
cat <<'EOF'
# GRUB Authentication
set superusers="grub"
password_pbkdf2 grub grub.pbkdf2.sha512.10000.A4A6B06EFAB660C11DD8EBC3BE73C5AB5D763ED937060477DB533B3E7D60F1DE66C3AC12DA795B46762AB8C4A1911B69B94FFCD88FB4499938150405DCB116F8.35D290F5B8D2677AEE5E8BAB4DB133206D417F99A26B14EAB8D0A5379DCD3632F40037388C9D2CA3001E0D6A8B74837549970EEEAEC3420CE38E2236DE1A8565
EOF
END
# 设置进入正式系统不需要认证如进入单用户模式进行重置账号密码时需要进行认证。 (高敏感数据库系统不建议下述操作)
# 在 135 加入 -unrestricted ,例如, 此处与Ubuntu不同的是不加--user=grub
# 133 echo "menuentry $(echo "$title" | grub_quote)' ${CLASS} \$menuentry_id_option 'gnulinux-$version-$type- $boot_device_id' {" | sed "s/^/$submenu_indentation/"
# 134 else
# 135 echo "menuentry --unrestricted '$(echo "$os" | grub_quote)' ${CLASS} \$menuentry_id_option 'gnulinux-simple-$boot_devic e_id' {" | sed "s/^/$submenu_indentation/"
sed -i '/echo "$title" | grub_quote/ { s/menuentry /menuentry /;}' /etc/grub.d/10_linux
sed -i '/echo "$os" | grub_quote/ { s/menuentry /menuentry --unrestricted /;}' /etc/grub.d/10_linux
# CentOS 方式更新GRUB从而生成boot启动文件
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
# (9) 记录安全事件日志
log::info "[-] 记录安全事件日志"
touch /var/log/.history/adm&>/dev/null; chmod 755 /var/log/.history/adm
semanage fcontext -a -t security_t '/var/log/.history/adm'
restorecon -v '/var/log/.history/adm'&>/dev/null
egrep -q "^\s*\*\.err;kern.debug;daemon.notice\s+.+$" /etc/rsyslog.conf && sed -ri "s/^\s*\*\.err;kern.debug;daemon.notice\s+.+$/*.err;kern.debug;daemon.notice \/var\/log\/.history\/adm/" /etc/rsyslog.conf || echo "*.err;kern.debug;daemon.notice /var/log/.history/adm" >> /etc/rsyslog.conf
# (10) 配置自动屏幕锁定(适用于具备图形界面的设备), 非图形界面不需要执行
log::info "[-] 对于有图形界面的系统配置10分钟屏幕锁定"
# gconftool-2 --direct \
# --config-source xml:readwrite:/etc/gconf/gconf.xml.mandatory \
# --type bool \
# --set /apps/gnome-screensaver/idle_activation_enabled true \
# --set /apps/gnome-screensaver/lock_enabled true \
# --type int \
# --set /apps/gnome-screensaver/idle_delay 10 \
# --type string \
# --set /apps/gnome-screensaver/mode blank-only
# (10) 关闭CentOS服务器中 SELINUX 以及防火墙端口放行
log::info "[-] SELINUX 禁用以及系统防火墙规则设置 "
sed -i "s/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/selinux/config
semanage port -m -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 20211 # 添加sshd服务20211端口到SELinux
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=20211/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=161/udp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
systemctl restart sshd
reboot
}
## 名称: os::Operation
## 用途: 操作系统安全运维设置相关脚本
## 参数: 无
os::Operation () {
log::info "[-] 操作系统安全运维设置相关脚本"
# (0) 禁用ctrl+alt+del组合键对系统重启 (必须要配置,我曾入过坑)
log::info "[-] 禁用控制台ctrl+alt+del组合键重启"
mv /usr/lib/systemd/system/ctrl-alt-del.target ${BACKUPDIR}/ctrl-alt-del.target-${EXECTIME}.bak
# (1) 设置文件删除回收站别名
log::info "[-] 设置文件删除回收站别名(防止误删文件) "
sudo tee -a /etc/profile.d/alias.sh <<'EOF'
# User specific aliases and functions
# 删除回收站
# find ~/.trash -delete
# 删除空目录
# find ~/.trash -type d -delete
alias rm="sh /usr/local/bin/remove.sh"
EOF
sudo tee /usr/local/bin/remove.sh <<'EOF'
#!/bin/sh
# 定义回收站文件夹目录.trash
trash="/.trash"
deltime=$(date +%Y%m%d-%H-%M-%S)
TRASH_DIR="${HOME}${trash}/${deltime}"
# 建立回收站目录当不存在的时候
if [ ! -e ${TRASH_DIR} ];then
mkdir -p ${TRASH_DIR}
fi
for i in $*;do
if [ "$i" = "-rf" ];then continue;fi
# 防止误操作
if [ "$i" = "/" ];then echo '# Danger delete command, Not delete / directory!';exit -1;fi
#定义秒时间戳
STAMP=$(date +%s)
#得到文件名称(非文件夹),参考man basename
fileName=$(basename $i)
#将输入的参数,对应文件mv至.trash目录,文件后缀,为当前的时间戳
mv $i ${TRASH_DIR}/${fileName}.${STAMP}
done
EOF
sudo chmod +775 /usr/local/bin/remove.sh /etc/profile.d/alias.sh /etc/profile.d/history-record.sh
sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/remove.sh /etc/profile.d/alias.sh /etc/profile.d/history-record.sh
source /etc/profile.d/alias.sh /etc/profile.d/history-record.sh
}
## 名称: os::DisableService
## 用途: 禁用与设置操作系统中某些服务(需要根据实际环境进行)
## 参数: 无
os::DisableService () {
log::info "[-] 禁用操作系统中某些服务(需要根据实际环境进行配置)"
log::info "[-] 配置禁用telnet服务"
cp /etc/services ${BACKUPDIR}/'services-'${EXECTIME}.bak
egrep -q "^\s*telnet\s+\d*.+$" /etc/services && sed -ri "/^\s*telnet\s+\d*.+$/s/^/# /" /etc/services
log::info "[-] 禁止匿名与root用户用户登录FTP"
if [ -f /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf ];then
cp /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd/'vsftpd.conf-'`date +%Y%m%d`.bak
systemctl list-unit-files|grep vsftpd > /dev/null && sed -ri "/^\s*anonymous_enable\s*\W+.+$/s/^/#/" /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf && echo "anonymous_enable=NO" >> /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
systemctl list-unit-files|grep vsftpd > /dev/null && echo "root" >> /etc/vsftpd/ftpusers
log::info "[-] 限制FTP用户上传的文件所具有的权限"
systemctl list-unit-files|grep vsftpd > /dev/null && sed -ri "/^\s*write_enable\s*\W+.+$/s/^/#/" /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf && echo "write_enable=NO" >> /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
systemctl list-unit-files|grep vsftpd > /dev/null && sed -ri "/^\s*ls_recurse_enable\s*\W+.+$/s/^/#/" /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf && echo "ls_recurse_enable=NO" >> /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
systemctl list-unit-files|grep vsftpd > /dev/null && sed -ri "/^\s*anon_umask\s*\W+.+$/s/^/#/" /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf && echo "anon_umask=077" >> /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
systemctl list-unit-files|grep vsftpd > /dev/null && sed -ri "/^\s*local_umask\s*\W+.+$/s/^/#/" /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf && echo "local_umask=022" >> /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
log::info "[-] 限制FTP用户登录后能访问的目录"
systemctl list-unit-files|grep vsftpd > /dev/null && sed -ri "/^\s*chroot_local_user\s*\W+.+$/s/^/#/" /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf && echo "chroot_local_user=NO" >> /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
log::info "[-] FTP Banner 设置"
systemctl list-unit-files|grep vsftpd > /dev/null && sed -ri "/^\s*ftpd_banner\s*\W+.+$/s/^/#/" /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf && echo "ftpd_banner='Authorized only. All activity will be monitored and reported.'" >> /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
log::info "[-] 限制不必要的服务 (根据实际环境配置)"
# systemctl disable rsh&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null;systemctl disable talk&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null;systemctl disable telnet&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null;systemctl disable tftp&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null;systemctl disable rsync&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null;systemctl disable xinetd&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null;systemctl disable nfs&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null;systemctl disable nfslock&>/dev/null 2&>/dev/null
fi
log::info "[-] 配置SNMP默认团体字"
if [ -f /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf ];then
cp /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf ${BACKUPDIR}/'snmpd.conf-'${EXECTIME}.bak
cat > /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf <<EOF
com2sec $SNMP_user default $SNMP_password
group $SNMP_group v1 $SNMP_user
group $SNMP_group v2c $SNMP_user
view systemview included .1 80
view systemview included .1.3.6.1.2.1.1
view systemview included .1.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.1
view $SNMP_view included .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.80
access $SNMP_group "" any noauth exact systemview none none
access $SNMP_group "" any noauth exact $SNMP_view none none
dontLogTCPWrappersConnects yes
trapcommunity $SNMP_password
authtrapenable 1
trap2sink $SNMP_ip
agentSecName $SNMP_user
rouser $SNMP_user
defaultMonitors yes
linkUpDownNotifications yes
EOF
fi
}
## 名称: os::optimizationn
## 用途: 操作系统优化设置(内核参数)
## 参数: 无
os::Optimizationn () {
log::info "[-] 正在进行操作系统内核参数优化设置......."
# (1) 系统内核参数的配置(/etc/sysctl.conf)
log::info "[-] 系统内核参数的配置/etc/sysctl.conf"
# /etc/sysctl.d/99-kubernetes-cri.conf
egrep -q "^(#)?net.ipv4.ip_forward.*" /etc/sysctl.conf && sed -ri "s|^(#)?net.ipv4.ip_forward.*|net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1|g" /etc/sysctl.conf || echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
# egrep -q "^(#)?net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables.*" /etc/sysctl.conf && sed -ri "s|^(#)?net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables.*|net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1|g" /etc/sysctl.conf || echo "net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
# egrep -q "^(#)?net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables.*" /etc/sysctl.conf && sed -ri "s|^(#)?net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables.*|net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1|g" /etc/sysctl.conf || echo "net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
egrep -q "^(#)?net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6.*" /etc/sysctl.conf && sed -ri "s|^(#)?net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6.*|net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1|g" /etc/sysctl.conf || echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
egrep -q "^(#)?net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6.*" /etc/sysctl.conf && sed -ri "s|^(#)?net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6.*|net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1|g" /etc/sysctl.conf || echo "net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
egrep -q "^(#)?net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6.*" /etc/sysctl.conf && sed -ri "s|^(#)?net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6.*|net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1|g" /etc/sysctl.conf || echo "net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
egrep -q "^(#)?net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding.*" /etc/sysctl.conf && sed -ri "s|^(#)?net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding.*|net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding = 1|g" /etc/sysctl.conf || echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
egrep -q "^(#)?vm.max_map_count.*" /etc/sysctl.conf && sed -ri "s|^(#)?vm.max_map_count.*|vm.max_map_count = 262144|g" /etc/sysctl.conf || echo "vm.max_map_count = 262144" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf <<'EOF'
# 调整提升服务器负载能力之外,还能够防御小流量的Dos、CC和SYN攻击
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
# net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 60
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_fastopen = 3
# 优化TCP的可使用端口范围及提升服务器并发能力(注意一般流量小的服务器上没必要设置如下参数)
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 1200
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 8192
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 5000
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65535
# 优化核套接字TCP的缓存区
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 8192
net.core.somaxconn = 8192
net.core.rmem_max = 12582912
net.core.rmem_default = 6291456
net.core.wmem_max = 12582912
net.core.wmem_default = 6291456
EOF
# (2) Linux 系统的最大进程数和最大文件打开数限制
log::info "[-] Linux 系统的最大进程数和最大文件打开数限制 "
egrep -q "^\s*ulimit -HSn\s+\w+.*$" /etc/profile && sed -ri "s/^\s*ulimit -HSn\s+\w+.*$/ulimit -HSn 65535/" /etc/profile || echo "ulimit -HSn 65535" >> /etc/profile
egrep -q "^\s*ulimit -HSu\s+\w+.*$" /etc/profile && sed -ri "s/^\s*ulimit -HSu\s+\w+.*$/ulimit -HSu 65535/" /etc/profile || echo "ulimit -HSu 65535" >> /etc/profile
sed -i "/# End/i * soft nofile 65535" /etc/security/limits.conf
sed -i "/# End/i * hard nofile 65535" /etc/security/limits.conf
sed -i "/# End/i * soft nproc 65535" /etc/security/limits.conf
sed -i "/# End/i * hard nproc 65535" /etc/security/limits.conf
sysctl -p
# 需重启生效
reboot
}
## 名称: os::Swap
## 用途: Liunx 系统创建SWAP交换分区(默认2G)
## 参数: $1(几G)
os::Swap () {
if [ -e $1 ];then
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1024 count=2097152 # 2G Swap 分区 1024 * 1024 , centos 以 1000 为标准
else
number=$(echo "${1}*1024*1024"|bc)
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1024 count=${number} # 2G Swap 分区 1024 * 1024 , centos 以 1000 为标准
fi
sudo mkswap /swapfile && sudo swapon /swapfile
if [ $(grep -c "/swapfile" /etc/fstab) -eq 0 ];then
sudo tee -a /etc/fstab <<'EOF'
/swapfile swap swap default 0 0
EOF
fi
sudo swapon --show && sudo free -h
}
## 名称: software::Java
## 用途: java 环境安装与设置
## 参数: 无
software::Java () {
# 基础变量
JAVA_FILE="/root/Downloads/jdk-8u211-linux-x64.tar.gz"
JAVA_SRC="/usr/local/"
JAVA_DIR="/usr/local/jdk"
# 环境配置
sudo tar -zxvf ${JAVA_FILE} -C ${JAVA_SRC}
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/jdk
JAVA_SRC=$(ls /usr/local/ | grep "jdk")
sudo ln -s ${JAVA_SRC} ${JAVA_DIR}
export PATH=${JAVA_DIR}/bin:${PATH}
sudo cp /etc/profile /etc/profile.$(date +%Y%m%d-%H%M%S).bak
sudo tee -a /etc/profile <<'EOF'
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk
export JRE_HOME=/usr/local/jdk/jre
export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
EOF
java -version
}
## 名称: disk::Lvsmanager
## 用途: CentOS7 操作系统磁盘 LVS 逻辑卷添加与配置(扩容流程)
## 参数: 无
disk::lvsmanager () {
echo "\n分区信息:"
sudo df -Th
sudo lsblk
echo -e "\n 磁盘信息:"
sudo fdisk -l
echo -e "\n PV物理卷查看:"
sudo pvscan
echo -e "\n vgs虚拟卷查看:"
sudo vgs
echo -e "\n lvscan逻辑卷扫描:"
sudo lvscan
echo -e "\n 分区扩展"
echo "CentOS \n lvextend -L +24G /dev/centos/root"
echo "lsblk"
echo -e "Centos \n # xfs_growfs /dev/mapper/centos-root"
}
# 安全加固过程临时文件清理为基线镜像做准备
unalias rm
find ~/.trash/* -delete
find /home/ -type d -name .trash -exec find {} -delete \;
find /var/log -name "*.gz" -delete
find /var/log -name "*log.*" -delete
find /var/log -name "vmware-*.*.log" -delete
find /var/log -name "*.log" -exec truncate -s 0 {} \;
find /var/log -name "system@*" -delete
find /var/log -name "user-1000@*" -delete
find /tmp/* -delete
至此 CentOS7 安全加固脚本完毕。
原文地址: Linux与Windows服务器操作系统安全防御实践指南 ( https://blog.weiyigeek.top/2020/10-13-585.html )
本文章来源 我的Blog站点 或 WeiyiGeek 公众账号 以及 我的BiliBili专栏 (
技术交流、友链交换请邮我哟),谢谢支持!(๑′ᴗ‵๑) ❤
这篇关于如何利用Shell脚本进行Linux服务器之CentOS7系统初始化及其安全加固(适用于等保2.0)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对大家有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持为之网!
- 2024-12-22初创企业的效率秘诀!实用的看板式任务管理工具推荐
- 2024-12-22新能源汽车销售难题如何破?看板工具助力门店管理升级
- 2024-12-218 款现代无代码工具,轻松提升开发者工作效率 ???????
- 2024-12-21从线索跟踪到业绩提升:销售任务管理系统推荐
- 2024-12-21刚刚发布RobinReach:多渠道社交媒体管理工具 ??
- 2024-12-21跨地域协作无压力!推荐几款必备的可视化协同工具
- 2024-12-21初学者指南:轻松掌握文章编辑器
- 2024-12-21Excel数据导出教程:让数据迁移变得简单
- 2024-12-21Excel数据导入入门教程
- 2024-12-215分钟速览:优化项目管理必备的5款高效工具